The Web3 Revolution: Transforming the Ecommerce Landscape
In an ever-expanding e-commerce environment, the Web3 technology has the potential to transform the way online commerce operates. The next generation of internet infrastructure is capable of creating new economic models that could revolutionize the $5 billion global ecommerce market. But what exactly is Web3, and how will it reshape the businesses that sell products and services online?
Understanding Web3: The Internet's New Frontier
Web3 represents the third major iteration of the internet. Let’s go back to the beginning: Web1 offered static, read-only content; Web2 introduced interactive, user-generated content controlled by centralized platforms. Unfolding before our eyes, Web3 is a decentralized internet built on blockchain technology. This new paradigm shifts control from tech giants to users, enabling peer-to-peer interactions without intermediaries. This diagram from GoodFirms shows the transition from Web1 to Web3:
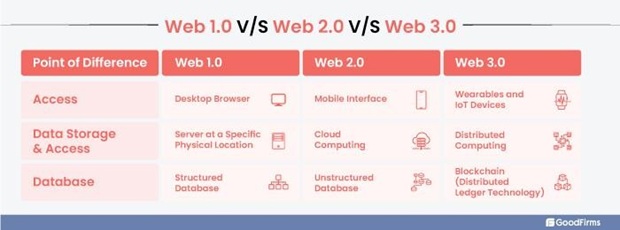
At its core, Web3 is characterized by:
- Decentralization: Replacing central authorities with distributed networks
- Blockchain Technology: Transparent, immutable record-keeping
- Token Economics: Digital assets and cryptocurrencies enabling new ownership models
- Self-Sovereign Identity: User control over personal data
- Trustless Systems: Protocols that don't require third-party verification
These foundational elements open up new opportunities for reimagining e-commerce from the ground up. This allows us to rebalance the current system and eliminate all aspects of long-standing inefficiencies.
How Web3 Will Transform Ecommerce
Looking ahead, Web3 is framed to redefine ecommerce in several ways.
1. Revolutionizing Payments
Cryptocurrency payments eliminate many of the friction points in traditional ecommerce transactions. Cross-border payments become nearly instantaneous and virtually fee-free, opening global markets to merchants previously excluded by banking limitations or excessive transaction costs.
This is exactly what crypto tokens like XRP were designed for. XRP was created to help banks move money quickly, securely, and cheaply anywhere in the world. Because of this, XRP has become the 3rd largest cryptocurrency with a market cap of $127.06B as of February 27, 2025, according to Binance. Digital currencies like XRP become crucial in the Web3 environment, giving consumers and businesses the ability to transact across borders and without the interference of centralized financial institutions.
Micropayments, previously impractical due to processing fees, become viable in a Web3 environment. This enables new business models for digital content, services, and products. A consumer might pay fractions of a cent to read an article, use an app for a few minutes, or access a small digital service—impossible in the current payment infrastructure.
2. Eliminating Intermediaries
Today's online marketplaces extract substantial fees from merchants. We can say that platforms like Amazon, eBay act as intermediaries, building a bridge of communication. They control access to customers and set the terms for sellers. The most significant change that Web3 brings to e-commerce is the removal of this intermediary.
Web3's decentralized protocols enable direct peer-to-peer commerce. Smart contracts mean the self-executing agreements with terms written in code so they can automatically enforce transaction terms without requiring trust in a third party. This creates an equitable business model. Implementing such a process transformation can significantly reduce costs for merchants and prices for consumers.
3. Redefining Customer Relationships
Web3 creates new possibilities for customer engagement through tokenization. Brands can issue different kinds of tokens. They could represent ownership, access, or loyalty. All that create innovative ways to build community and reward customers.
NFTs (Non-Fungible Tokens) enable digital scarcity and provable ownership of virtual and physical goods. A luxury fashion brand might issue NFTs to authenticate physical products. At the same time, a gaming company could create truly ownable in-game assets tradeable across platforms.
Tokenized loyalty programs can be a viable alternative to traditional systems. Instead of accumulating points in siloed brand ecosystems, customers can earn tokens with real value and transferability, changing the dynamics of customer retention.
4. Transforming Supply Chain Management
The main advantage of blockchain technology is that it provides unprecedented transparency for supply chains. Immutable records that can track products from manufacturing to delivery can also verify their authenticity. In addition, ethical sourcing and environmental compliance can be easily tracked.
Smart contracts can automate payments to suppliers. For example, the new technology allows payments to be made after verified delivery. This can reduce payment delays that affect the sustainability of small businesses. Such automation extends to inventory management, with decentralized systems potentially coordinating production based on real-time demand signals.
Processes Ripe for Disruption
There are several key ecommerce processes that stand to be fundamentally transformed by Web3 technologies.
- Payment Processing: Credit card networks and payment processors charging 2-3% per transaction face competition from cryptocurrency payment rails with negligible fees.
- Identity Verification: Self-sovereign identity solutions could replace repetitive account creation and KYC processes, putting users in control of their personal data.
- Product Authentication: Blockchain verification could disrupt the $1.8 trillion counterfeit goods market by providing irrefutable proof of authenticity.
- Digital Advertising: Token-based attention models could replace the surveillance capitalism of current digital marketing, compensating users directly for their attention.
- Customer Data Management: Decentralized data storage with user permission systems could replace centralized databases vulnerable to breaches.
The Future Direction of Web3 Ecommerce
Looking forward, there are several trends that will likely shape Web3's impact on ecommerce.
- Hybrid Models: Rather than complete disruption, many successful implementations will blend Web2 and Web3 elements, gradually introducing tokenization and decentralization to existing platforms.
- Metaverse Integration: Virtual worlds will converge with ecommerce, creating immersive shopping experiences where blockchain-verified digital items have real value.
- AI: Decentralized AI models will enable personalized shopping experiences without compromising user data sovereignty.
- Tokenized Physical Assets: Real-world products increasingly linked to digital tokens will create new ownership models and secondary markets.
- Decentralized Autonomous Retail: DAOs may emerge as a new corporate structure for community-owned marketplaces and brands.
Conclusion
Web3 represents a huge opportunity for the ecommerce ecosystem. However, it will take a long time to implement and refine. Full transformation will take time. But it is already clear that the foundations for a more open and fair online commerce are being laid.
Forward-thinking brands and retailers are already experimenting with blockchain systems, implementing new token-based loyalty systems, and many have added cryptocurrency payments to their existing payment methods. Those who understand and embrace these technologies early will help shape the next generation of ecommerce, potentially leading the way.
The transition will not be immediate or complete. Many Web2 ecommerce models will survive alongside Web3 innovations. But the long-term trajectory is toward a more decentralized, user-controlled commerce internet, where value flows more directly between buyers and sellers. For the ecommerce industry, adaptation to this new paradigm isn't just an opportunity; it's increasingly becoming an imperative.
Copyright © . All Rights Reserved
